Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a prevalent condition affecting 45% of the UK adult population; around 10% are affected by the most severe form (Adult Dental Health Survey, 2009). Periodontal disease is characterised by inflammation and destruction of the tissues and structures which support and hold teeth in place (Marsh, 2010).
People with diabetes have an increased risk of periodontal disease (Löe, 1993). A recent survey showed that 33% of people living with diabetes are unaware that it can affect their gum health, yet 75% of people in the survey reported having bleeding gums (Woodfield, 2017). The early signs of periodontal disease can often be asymptomatic, however, especially in people who smoke. People with diabetes are therefore encouraged to visit their dentist regularly and maintain excellent plaque removal from their teeth to prevent the initiation and progression of periodontal disease.
Periodontal disease has a bidirectional relationship with diabetes (Casanova et al, 2014), meaning that the presence of one disease can influence the presentation of the other and vice versa. Also, optimal management and treatment of one disease may influence the presentation and response to treatment of the other in both directions (Simpson et al, 2015).
How periodontal disease starts and progresses
Health
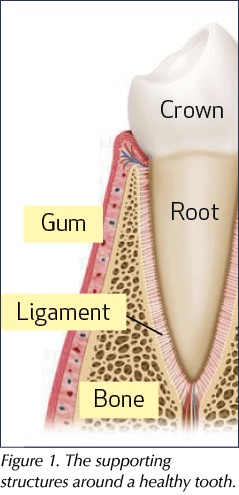
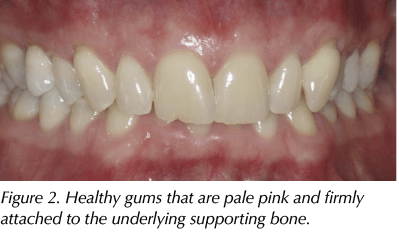
The periodontium is made up of gingival (gum) tissues, the supporting bone and a periodontal ligament that attaches the root of the tooth to the bone (Figure 1). The periodontium plays an important role in keeping the teeth in place (Eaton and Ower, 2015). A healthy periodontium (Figure 2), is key to a healthy mouth and body. It enables a person to eat, speak and smile, as well as improving a person’s self-esteem and quality of life.
Initiation of periodontal disease
Throughout the day, dental plaque builds up on the tooth surfaces. This is a sticky white film made up of bacteria, saliva and food. The aim of tooth brushing is to remove this layer of dental plaque twice a day. If dental plaque is not effectively removed from the tooth surfaces, especially at the junction where the tooth meets the gum, the dental plaque can irritate the gum tissues leading to inflammation, known as gingivitis (Marsh, 2010).
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is characterised by red, swollen, bleeding and tender gums (Figure 3), and bad breath. It is reversible if effective plaque removal is resumed (Löe et al, 1965; Figure 4). If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis in susceptible individuals (Silva et al, 2015).
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is characterised by destruction of the bone and other supporting periodontal tissues, which can be detected clinically and radiographically (Marsh, 1994). Common signs and symptoms of periodontitis include all the signs of gingivitis, plus receding gums, painful abscesses, gaps between teeth, teeth drifting apart, loose teeth and eventual tooth loss (Figure 5).
There are different forms of inflammatory periodontal disease, some of which progress faster than others, leading to more severe breakdown of periodontal tissues supporting the tooth structures (Figure 6). Those who are susceptible to the severe form of periodontitis include people with uncontrolled diabetes, smokers and people who have a family history of gum disease (Grossi et al, 1995).
Although periodontitis leads to irreversible destruction of the supporting tissues of the teeth, in many cases the disease can be stabilised with effective treatment (see Figure 7). Periodontal treatment varies according to each individual; however, it usually involves assisting patients with plaque removal and an intensive course of cleaning of the teeth both above and below the gum margin.
Periodontal disease and diabetes: A bidirectional relationship
Diabetes is characterised by a state of hyperglycaemia due to the absolute or relative deficiency in insulin production. A person with diabetes has an increased risk of periodontal disease, especially if the diabetes is poorly controlled (Botero et al, 2012). The increase in blood glucose that occurs in diabetes can cause damage to the nerves, blood vessels, heart, kidneys and eyes. In the same way, the periodontal tissues can also be affected. The reduced oxygen and nutrient levels that occur in the gums as a result of damage to the blood vessels make patients more susceptible to infection by the plaque bacteria. Poorly controlled blood glucose levels also lead to a rise in glucose in the saliva, which feeds the bacteria and increases the formation of dental plaque.
In the other direction, the presence of severe periodontitis has been shown to increase the risk of hyperglycaemia in people with diabetes and compromise glycaemic control in people without diabetes (Demmer et al, 2010; Casanova et al, 2014). The inflammation that occurs in the periodontal tissues escapes into the bloodstream and upsets the body’s immune system, which in turn affects blood glucose control.
Treatment
If a patient has both diabetes and periodontal disease, optimal management and treatment of one disease can improve the presentation and response to treatment of the other and vice versa (Simpson et al, 2015). Even in people who do not have diabetes, treatment of periodontal disease can improve blood glucose levels.
Improving knowledge of oral health in people living with diabetes
People with diabetes are often unaware of its possible effect on their oral and periodontal health. Healthcare providers, including diabetes specialist nurses, practice nurses, GPs and healthcare assistants, are encouraged to inform both newly diagnosed and long-standing diabetes patients about their increased risk of gum disease. Box 1 lists the oral health advice that should be given to patients with diabetes.
Other oral problems that can occur in people with diabetes
For people with diabetes, sugar may be an important part of the diet, especially if hypoglycaemia is commonplace. This can increase the risk of tooth decay (caries). To prevent tooth decay, patients are encouraged to use fluoride toothpaste when they brush their teeth and reduce the frequency of sugary food and drink consumption where possible.
Some medications prescribed for the treatment of diabetes can cause xerostomia (dry mouth) because of reduced salivary flow. A dry mouth increases the risk of oral thrush, tooth decay, periodontal disease and halitosis. A dentist or GP can prescribe salivary substitutes and a high-fluoride toothpaste to alleviate these effects.
Discussion and conclusion
Periodontal disease has been linked to 57 systemic diseases (Loos, 2016), and a strong association between periodontal disease and diabetes has been confirmed. Oral health is not currently included in the DESMOND (Diabetes Education and Self Management for Ongoing and Newly Diagnosed)course. Its importance in the management of diabetes is not well known and is therefore undervalued by medical and dental practitioners as a whole.
Due to the bidirectional relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease, people with diabetes should be informed about the increased risk of periodontal disease and encouraged to maintain good oral health. By regularly attending a dentist or hygienist, patients can be screened for early signs of periodontal disease, which are commonly asymptomatic. Periodontal research calls for large randomised controlled trials to further investigate the effect of treatment of periodontal disease on blood glucose control in people with diabetes.
Further information and resources
British Society of Periodontology
www.bsperio.org.uk has a section on periodontal disease and diabetes for professionals with articles and information leaflets. The patient information leaflet Periodontal health for better life and infographics to increase patient and healthcare worker awareness, produced as part of the joint 2017 campaign with diabetes.co.uk, are available at: https://bit.ly/2Jsy7Q6
International consensus statement
Sanz M, Ceriello A, Buysschaert M et al (2018) Scientific evidence on the links between periodontal diseases and diabetes: Consensus report and guidelines of the joint workshop on periodontal diseases and diabetes by the International diabetes Federation and the European Federation of Periodontology. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 137: 231–41
Finding a dentist
If not registered with an NHS dentist, people living with diabetes can find one through their local area teams in England, NHS board in Scotland, local health board in Wales, or Health and Social Care Trust in Northern Ireland.











Developments that will impact your practice.
29 Aug 2025