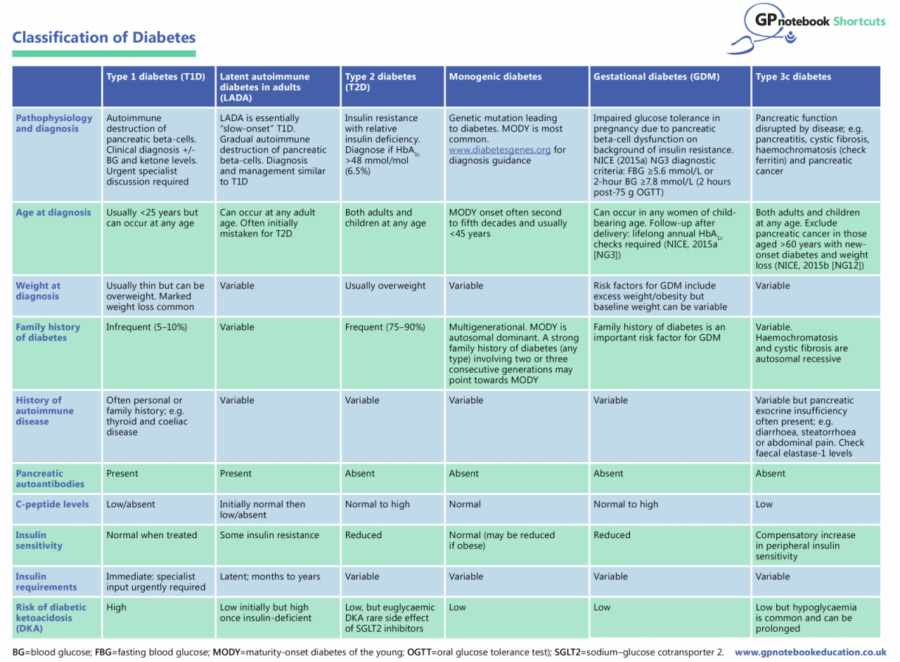
Type 1 diabetes is characterised by insulin deficiency brought about by autoimmune-mediated destruction of the pancreatic beta-cells. Although type 1 diabetes is commonly thought to first develop predominantly in younger people, genetic stratification analysis suggests that at least 40% of cases occur after the age of 30 years (Thomas et al, 2018). Most of these cases are characterised by severe insulin deficiency, with 89% needing insulin therapy after 1 year.
Type 1 diabetes can easily be misdiagnosed if it develops outside of childhood, as a recent study from the University of Exeter demonstrates (Thomas et al, 2019). The authors reviewed 583 people who were diagnosed with any type of diabetes after 30 years of age and who received insulin therapy. Overall, 21% of these had severe insulin deficiency and met the criteria for type 1 diabetes. They had similar clinical characteristics to a comparison cohort of 220 people with young-onset type 1 diabetes.
Overall, 38% of those with late-onset type 1 diabetes did not receive insulin at diagnosis; half of these were misdiagnosed as having type 2 diabetes. Early progression to insulin was a strong predictor of type 1 diabetes, with 85% of the type 1 cohort receving insulin within 1 year; furthermore, 47% of those who required insulin within 3 years of diagnosis had type 1 diabetes. BMI was not a robust identifier of late-onset type 1 diabetes: only 41% had a BMI <25 kg/m2, and 28% of those with type 2 diabetes had a BMI <25 kg/m2.
Classification of diabetes: A GPnotebook Shortcut
If misdiagnosed, people with late-onset type 1 diabetes will not receive appropriate education and may not be eligible for interventions such as carbohydrate counting courses, continuous glucose monitoring and insulin pump therapy; therefore, it is vital to correctly identify the condition. Anyone who is diagnosed with type 2 diabetes but progresses to insulin therapy within 3 years should strongly consider a C-peptide test to confirm the diagnosis – even if this requires referral or liaison with secondary care colleagues if the test cannot be ordered in primary care.
The diagnosis and classification of diabetes in primary care is increasingly challenging. The GPnotebook Shortcut overleaf will help in establishing the right diagnosis and ultimately to avoid any harm.

GPnotebook Shortcuts
GPnotebook Shortcuts are a series of easily digestible, bite-sized resources to help clinicians manage their patients in primary care. A full list of Shortcuts can be found here.
GPnotebook Education
GPnotebook Education is an independent educational resource which has been created with primary care professionals in mind and mirrors the daily work in primary care, using multiple patient case studies to cover latest clinical guidance, research and hot topics.
All GPnotebook Education courses provide unbiased, independent content, prepared and presented by fellow healthcare professionals. Visit gpnotebookeducation.com to learn more.



Risk of CVD and cardiovascular mortality differ between people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and between men and women.
2 Oct 2025