Ramadan is widely observed across the world. In the 2010 CREED study, 94.2% of participants with type 2 diabetes fasted for at least 15 days of Ramadan and 63.6% fasted for all the days (Babineaux et al, 2015). It is clear that fasting in Ramadan is a very important practice and has a major impact on the management of diabetes in Muslim populations (International Diabetes Federation and Diabetes and Ramadan International Alliance [IDF-DAR], 2021).
This year, Ramadan begins on the 10th/11th March, and it lasts for approximately one month. During Ramadan, the majority of Muslims observe absolute fasting between dawn and sunset throughout the month, abstaining not only from all food and drink but also from other practices such as smoking, and there are significant religious and psychological consequences for the person undertaking the fast (Lessan et al, 2021). The two main meals consumed are known as Iftar, the meal to break the fast; and Suhoor, the meal before the start of the fast.
The Qur’an allows individuals not to fast if they have an illness or medical condition (Bennakhi et al, 2021). Healthcare providers, members of the community, individuals with diabetes and their family, friends and carers should be made aware that those who are placed at high risk by fasting can be exempt, but they can also receive spiritual rewards by alternative steps like donations of food or helping the poor with money, also known as Fidya.
In the UK, fasting is commonly observed in the South Asian, Arabic and North African communities, and individuals from these communities require tailored medical and dietary advice prior to Ramadan (Hanif et al, 2020).
Ramadan is a festive period for many communities across the globe, and food is also a symbolic part of the fast, and it is common for participants to enjoy meals together and distribute traditional foods and sweets. Traditionally, the fast is ended by having a few dates followed by a lavish spread of foods. Many people will overindulge in foods and drinks that are high in calories and sugar, and can risk hyperglycaemia, when the fast is broken at the end of the day (Ahmed et al, 2012).
Risk avoidance during Ramadan
Fasting during Ramadan has a number of physical effects on the body. In people with diabetes, these changes, along with the type of medication being taken to treat diabetes, can contribute to a number of complications (Jabbar et al, 2021). These include:
- Hypoglycaemia, especially during the late period of fasting before the Iftar meal.
- Severe hyperglycaemia after each of the main meals (Iftar and Suhoor).
- Dehydration, especially in years with prolonged fasting hours and countries with hot climates.
Many diabetes-related risks can be minimised through medication adjustments and tailored nutrition advice. Therefore, it is crucial to increase awareness of these risks to allow safe participation in Ramadan fasting. The recently updated IDF-DAR (2021) guideline on diabetes and Ramadan provides both practical information and recommendations to help healthcare professionals optimise care and ensure that people with diabetes who plan to fast during Ramadan can do so safely. This includes a risk stratification table, with guidance on individuals who are at high, medium and low risk of fasting (Figure 1).
In the current pandemic, people in the low- or moderate-risk category, who are exposed to people with confirmed COVID-19, are safe to fast as long as they are asymptomatic. Those who develop symptoms whilst fasting should be advised to break the fast (Ahmed et al, 2020).
For people with type 2 diabetes at high risk, there is emerging evidence that newer technologies, such as isCGM (commonly known as flash), can help them fast with fewer complications (Lessan et al, 2015).
Although certain people with type 2 diabetes can be exempt from taking part in Ramadan, the majority will want to take part (Salti et al, 2004). They should not be deterred from fasting unnecessarily, as there are few harmful effects in the majority of people with diabetes, and Ramadan fasting can also have physical, emotional and spiritual benefits. Potential benefits and risks associated with fasting are listed in Table 1.
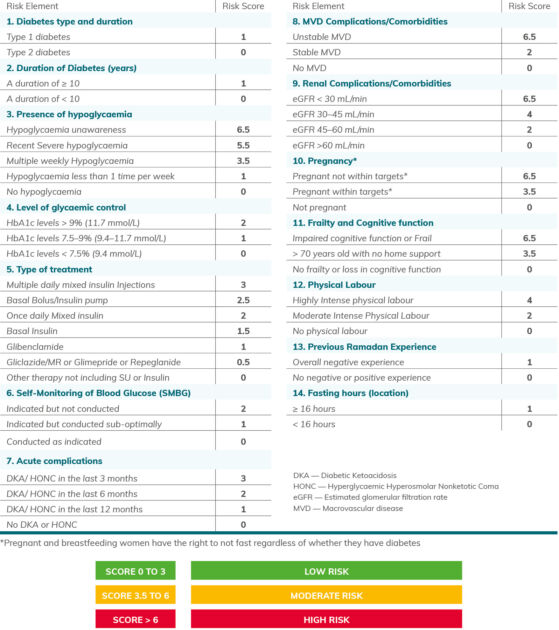
Figure 1. IDF-DAR (2021) Risk score and categories for Ramadan fasting (reused with permission).
Diabetes and Ramadan education
Diabetes self-management education and support addresses the practical, clinical, psychosocial and behavioural aspects of care needed for daily self-management, and is essential for safe fasting during Ramadan. The objective of Ramadan-focused education is to raise awareness of the risks associated with diabetes and fasting, and to provide strategies for effective prevention.
The clear benefits of structured education on many aspects of diabetes in Ramadan have been demonstrated in several studies, in diverse populations. A systematic review revealed a significant reduction in hypoglycaemia risk for fasting participants who received Ramadan‐focused education compared with those who received standard care, as well as a significant improvement in HbA1c (Tourkmanani et al, 2020).
Aims of pre-Ramadan education
The aims of structured education in preparation for Ramadan include the following:
- Modification and adjustment of nutrition plans for optimal glucose control during Ramadan.
- Designing nutrition plans that may help weight reduction for those aiming to lose weight during Ramadan.
- Adjustment of glucose-lowering medications to match nutrition and fasting.
- Encouragement to continue daily exercise and work activities.
- Recognition of warning symptoms of dehydration, hypoglycaemia and other possible complications.
- Informing of the need to break the fast if blood glucose falls below 3.9 mmol/L or rises above 16.6 mmol/L (Ahmedani et al, 2021).
- Informing of the need to monitor blood glucose regularly (blood glucose testing does not break the fast).
- Encouraging the monitoring of body weight during Ramadan.
The Ramadan Nutrition Plan
Nutrition therapy plays a vital role in diabetes management during Ramadan. Ramadan provides an ideal opportunity for people to channel their strength and discipline into adhering to healthy, nutritious and balanced meals at the Suhoor and Iftar meals.
An individual’s regional beliefs and culture should be considered when preparing their diet plan (Shaltout et al, 2020). Ramadan can result in an extra burden of calories; Iftar, the meal taken when the fast is broken at sunset, often turns into a feast, with huge volumes of food laden with sugar and carbohydrates. Since there is cultural variation in the traditional foods eaten at Iftar, a well-trained dietitian should be at the centre of the diabetes management and follow-up team. Example tailored meal plans from countries around the world, including Egypt, Malaysia, Indonesia, China, Pakistan and South Africa, are available in the IDF-DAR (2021) guideline.
The structure of the IDF-DAR Ramadan Nutrition Plan has been shown to improve fasting blood glucose and triglyceride levels, and self-monitoring glucose at pre-dawn and pre-bed, than standard care in patients with type 2 diabetes. Indeed, knowledge of individualised meal plans has shown to improve outcomes, by helping to maintain optimal glycaemic control, during the month of Ramadan and throughout the year (Mohd Yusof et al, 2020).
The key concepts of the Ramadan Nutrition plan are summarised in Box 1, and are outlined in more detail below.

Foods to recommend during Suhoor
For Suhoor (the pre-dawn meal), meals needs to be wholesome to provide enough energy to last the long hours of fasting and should include the following foods.
Complex carbohydrates: Eat meals based around small portions of carbohydrates. Have wholegrain sources of starchy carbohydrates, such as granary bread, wholegrain cereals, lentils, oats, quinoa, buckwheat, bulgur wheat and couscous. These foods release energy slowly, which can help maintain blood glucose levels and make individuals feel less hungry.
Fruits and vegetables: Rich in fibre, fruits and vegetables are essential for fasting as they increase the feeling of fullness and keep the person hydrated. Include fruits such as watermelon and kiwis, and vegetables such as cucumber. Fruits and vegetables provide fibre and reduce risk of constipation. Include more non-starchy vegetables such as green beans, courgettes, aubergines and mushrooms, and fruits including berries.
Protein-rich foods: Include some source of protein, such as eggs, lentils, beans or chickpeas. Protein foods are an essential part of the diet and help to keep people feeling full whilst also having less impact on blood glucose levels.
Dairy foods: Try to include yoghurts or milk-based foods at both Suhoor and Iftar to ensure sufficient calcium levels. Try plain yoghurts with nuts and fruits such as berries, or use milk and yoghurt to make milky drinks or smoothies with berries. Those who are lactose intolerant can choose lactose-free milk or calcium-fortified soya milk.
Fluids: Drink plenty of water at Suhoor. Avoid drinks that contain caffeine, such as tea and coffee, as these can make the person lose more water by going to the toilet more. Avoid sugary drinks such as orange, apple and tropical fruit juice and fizzy drinks. Non-sweetened drinks such as unsweetened lassi or laban are a preferred option.
Foods to recommend during Iftar
Iftar (the sunset meal) is the time when the person replenishes energy levels, so every effort should be made to consume foods from all major food groups. Iftar also needs to provide a quick release of enough energy. Iftar should include the following foods.
Dates: Traditionally during Ramadan, dates are eaten at the start of Iftar to symbolise the breaking of the fast. They are a quick source of energy and are high in fibre, calcium and iron. However, the number eaten should be limited as dates are high in sugar.
Complex carbohydrates: It is recommended to eat meals based around small portions of starchy carbohydrates, such as whole grains, rice or flatbread, in small portions. Have wholegrain sources of starchy carbohydrates, such as lentils, quinoa, buckwheat, bulgur wheat and couscous.
Meats and alternatives: Incorporate protein-rich sources, such as lean meat, skinless chicken, fish, eggs, legumes and low-fat dairy products.
Healthy meals: Avoid the usage of deep-fat fryers during Ramadan. When using oil for cooking, try to measure oil and avoid deep frying. Reheating oil increases the amount of trans-fatty acids, which are bad for the heart. Limit the number of starters at Iftar, especially if based around fried snacks such as samosas. Any starters should be based around salads, fruits, lentils or soups, to leave room for the main healthy meal of the day.
Reduce intake of processed foods: Avoid deep-fried foods and those that contain refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pastries, biscuits and baklava. Avoid processed meats, burgers, fried chicken and chips. Have small amounts of foods like baklava and halwa (made with semolina, butter and sugar).
Salt: Reduce intake of salt and salted food, including dressings, sauces, salted nuts and crisps. Dehydration is a risk due to limited fluid intake during the day, and high-salt foods can further increase this risk.
Fluids: Drink plenty of water at Iftar. It is recommended to drink at least eight cups of water between Iftar and Suhoor, so that the body may adjust fluid levels in time for the next day. Again, avoid drinks that contain caffeine, such as tea and coffee, as these can make the person lose more water by going to the toilet more. Avoid sugary drinks such as orange, apple and tropical fruit juice and fizzy drinks. Non-sweetened drinks such as unsweetened lassi or laban are a preferred option.
Eid ul Fitr
After the month of Ramadan, there is the celebration of Eid ul Fitr. During this, people with type 2 diabetes should try to minimise or avoid intake of highly processed and fried foods, such as deep-fried snacks including samosas, pakoras, chips and fried potatoes, and minimise the intake of sugar-rich sweets such as baklava, halwa, kheer and Indian sweets.
The Ramadan Nutrition Plan (RNP) app
A mobile and web-based application is available from IDF-DAR to provide healthcare professionals with expert information and help them individualise meal plans for people with diabetes during Ramadan. A patient platform is also available that includes the diabetes nutrition plan, example meal plans for different countries and regions, and educational resources. This could be very useful for individuals seeking to fast during Ramadan, particularly for those who do not have access to appropriate care. It is available at: https://daralliance.me/#random-nutrition
Physical activity and fasting
People with type 2 diabetes may continue to exercise during the month of Ramadan and continue their daily routine, particularly in morning hours, but they should not exercise excessively one or two hours before Iftar. Although rigorous exercise is not recommended during fasting because of the increased risk of hypoglycaemia and dehydration, people with diabetes should be encouraged to take regular light-to-moderate exercise during Ramadan.
Individuals should be reminded that the physical exertions involved in Tarawih prayers, such as bowing, kneeling and rising, should be considered part of their daily exercise activities. They should also check their blood glucose levels if they feel unwell or faint, during or after exercise (Mohd Yusof et al, 2020).
Ramadan safety tips for people with type 2 diabetes
- Always carry glucose treatment with you.
- Test your blood regularly to monitor your glucose (sugar) levels. This will not break your fast.
- Test your blood glucose level if you feel unwell during the fast.
- If your blood glucose level is high or low, you must treat this.
- If your blood glucose is less than 3.9 mmol/L, end the fast immediately and treat the low blood glucose.
- If your blood glucose is higher than 16.6 mmol/L, end the fast immediately.
- If you become dehydrated, end the fast immediately and have a drink of water.
- If you start to feel unwell, disoriented or confused, or if you collapse or faint, you should stop fasting and have a drink of water or other fluid, and check your blood glucose levels.
- Insulin users should never stop your insulin, but you must speak to your doctor because you may need to change the dose and timing of your insulin injections.
- Keep meals well balanced and drink plenty of fluids during non-fasting hours.
Conclusions
This review provides an outline of Ramadan-focused structured education and culturally specific nutrition advice to give to people with type 2 diabetes. In recent years, pre-Ramadan nutrition advice has been identified as crucial for safe fasting among people with diabetes. Ramadan‐focused diabetes education has a significant impact on hypoglycaemia and glycaemic control, with no significant effect on body weight, blood lipids or blood pressure (Mohd Yusof et al, 2020). The IDF-DAR Diabetes and Ramadan Practical Guidelines provide healthcare professionals with the latest evidence-based recommendations, allowing them to deliver the best possible care and support for people with diabetes who wish to fast during Ramadan.
Summary of recommendations
- Adjust nutrition plans for optimal glucose control during Ramadan.
- People with diabetes intending to fast during Ramadan should be categorised into low, moderate and high risk.
- The implementation of guidelines requires effective communication with, and education of, all those involved.
- Education, communication and accessibility are all critical to the success of the guidance provided in this document.
- The Ramadan Nutrition Plan helps people with diabetes to minimise the risks associated with Ramadan fasting, such as hypoglycaemia, hyperglycaemia, and dehydration.
- The Ramadan Nutrition Plan provides examples of meal plans within target caloric levels.
- Design a structured education plan that may help weight reduction for those who aim to lose weight during Ramadan.




Study provides new clues to why this condition is more aggressive in young children.
14 Nov 2025