Psychological wellbeing constructs, such as positive affect, have been associated with better diabetes outcomes, especially glycaemic control (Massey et al, 2019). Ruiz-Aranda et al (2018) suggest that emotional distress, another psychological construct, plays a role in diabetes outcomes by influencing the acquisition and maintenance of health habits correlated with HbA1c outcomes.
Emotional distress has previously been correlated with quality of life (QoL) by Faridah et al (2017). QoL is a subjective concept of satisfaction with life and an overall sense of health and wellbeing. QoL can powerfully predict engagement with diabetes management, and thus influence long-term health outcomes (Rubin, 2000).
Identifying the factors involved in influencing HbA1c control will contribute towards the facilitation of effective and targeted interventions, which will improve the psychosocial health of children and young people (CYP) with diabetes (Hsu et al, 2018).
Materials and procedure
A total of 190 screening questionnaires were administered to CYP with diabetes, aged 8–16 years (mean, 13 years; standard deviation [SD], 2.4), as part of their routine annual review clinic. CYP attend one annual review appointment per year, as part of their diabetes care.
The sample was 52.6% male (n=100); most of our study sample (96.3%) had a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes (T1D; n=183). Type 2 diabetes (T2D; n=5) made up just 2.6% of the sample and maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY; n=2) comprised 1.1% of the sample. Data were collected between January 2017 and October 2019; some CYP are represented more than once in the data due to attending multiple annual review appointments during the study period (approximately 3 years).
The clinics were held in a district general hospital where CYP received their diabetes care; the sample is therefore opportunistic, comprising only CYP attending the clinic.
The Paediatric Index of Emotional Distress (PI-ED; O’Connor et al, 2016) was used to provide a reliable and valid measure of emotional distress in CYP aged 8–16 years, by measuring anxiety and depression within a paediatric setting. The PI-ED is a 14-item questionnaire that scores using a 4-point Likert scale (3=always, 2=a lot of the time, 1=sometimes, 0=not at all). Higher scores indicate higher levels of emotional distress; the PI-ED clinical threshold is 20.
The Paediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL Diabetes Module Version 3.0) is a brief, self-report screening tool for QoL. It consists of 28 items and five dimensions: Diabetes (11 items), Treatment I (4 items), Treatment II (7 items), Worry (3 items), and Communication (3 items). Each item is scored on a 5-point Likert scale (0=never, 1=almost never, 2=sometimes, 3=often, 4=almost always). The measures used were self-reported to eliminate the potential bias introduced by parent-proxy reports.
Blood analysis, via a Siemens DCA Vantage Analyser©, was conducted at each annual review to acquire an accurate HbA1c reading.
Statistical analyses were carried out on the data to determine the strength and direction of the relationships between QoL, emotional distress and HbA1c. Incomplete data sets were removed to maintain the psychometric integrity of the findings.
Results
Statistical analyses were used to examine the relationship between QoL (mean=324.82, SD=69.54), emotional distress (mean=10.69, SD=6.81), and HbA1c control (mean=64.11 mmol/mol, SD=14.28). The mean HbA1c level of this cohort of young people was above the target 48 mmol/mol, as recommended by NICE guidelines. Levels of emotional distress, as indicated by the mean PI-ED outcome, were below the clinical threshold. Moreover, higher scores on the PedsQL indicate a better QoL, therefore the scores indicate relatively good QoL.
Using a bivariate correlation, it was found that female participants had a higher mean HbA1c level (mean=66.03 mmol/mol, SD=14.73) than males (mean=62.37 mmol/mol, SD=13.71); however, the relationship was not statistically significant (r=–0.107; P=0.141). Females also reported higher levels of emotional distress (mean=11.14, SD=7.29) than male participants (mean=10.29, SD=6.37). In continuation, females reported a lower mean QoL (mean=313.12, SD=78.16) than males (mean=335.34, SD=59.19).
Furthermore, the data indicated a statistically significant positive correlation between age and HbA1c levels (r=0.18; P=0.016), suggesting that older CYP have higher HbA1c levels. This is supported by the outcomes demonstrating that 16-year-old service users had the highest mean HbA1c (mean=69.04 mmol/mol, SD=16.75), whereas 9-year-old children had the lowest (mean=56.1 mmol/mol, SD=8.95).
The Pearson correlation coefficient for HbA1c and emotional distress depicts a statistically significant, positive linear relationship (r=0.15; P=0.02), suggesting that those experiencing lower levels of emotional distress have lower HbA1c levels (Figure 1). As emotional distress scores increase, HbA1c levels also increase.
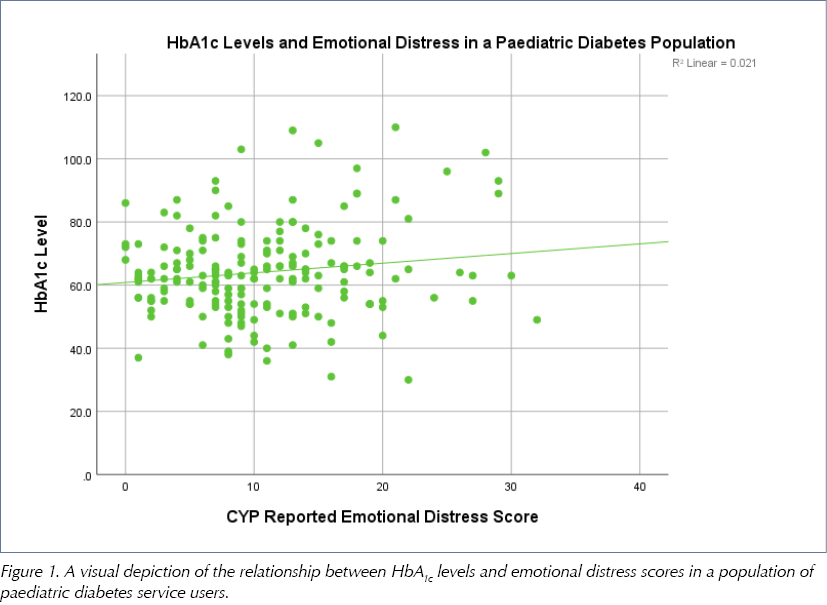
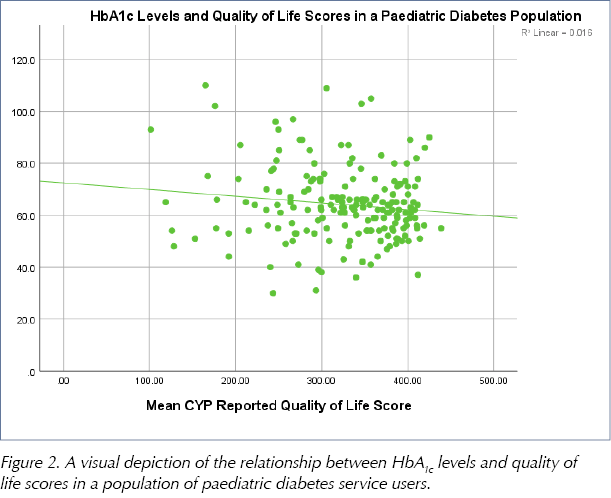
HbA1c and mean QoL scores also demonstrate a statistically significant relationship; however, it is a moderate, negative linear relationship (r=–0.13; P=0.04), suggesting that those with higher HbA1c levels have lower mean QoL scores (Figure 2). As HbA1c decreases, mean QoL scores increase.
Moreover, emotional distress and QoL demonstrated a statistically significant, moderate, negative linear relationship (r=–0.64; P<0.001), suggesting those with higher mean QoL scores experience lower levels of emotional distress.
Discussion
Despite advances in pharmacological treatment and intervention delivery, diabetes management remains a challenge for many CYP. The effects of diabetes and its management extend beyond purely medical outcomes. Suboptimal glycaemic control in CYP with diabetes is hypothesised to be associated with a lower reported QoL (Hassan et al, 2006), and an increased risk of emotional distress (Jones et al, 2015).
Considering the above, the aim of the present study was to correlate concepts of QoL and emotional distress with the clinical pictures of a sample of CYP with diabetes; it was hoped that this knowledge could facilitate the implementation of targeted and effective multidisciplinary team (MDT) intervention, as well as to inform other clinicians working in paediatric diabetes teams.
The mean HbA1c in this cohort of CYP was above the NICE-recommended threshold of 48 mmol/mol. Moreover, a significant positive correlation between age and HbA1c level was found, indicating declining HbA1c control as CYP develop. This relationship can be explained, in part, in the context of age and independence; the current sample’s mean age was 13 years old, the beginning of adolescence and independence. Parents and carers hold more responsibility for condition management in younger children, while adolescents are more independent (Nardi et al, 2008). Condition management is challenging and it is reported that only 20% of adolescents adhere fully to recommended condition management (Kyngäs, 2000).
It is important to acknowledge that children face multiple transitions as they age, including puberty, which can be emotionally distressing (Byrne et al, 2007). Future research should explore gender differences in the context of puberty and hormones, and how these correlate to emotional distress and QoL outcomes. This analysis would allow brief advice and information provided by medical teams to be individualised, more idealised, and attuned to the service user’s needs.
While the clinical outcomes of diabetes, such as HbA1c, are fundamental aspects of diabetes care, paediatric diabetes teams should adopt a holistic model of care (Goss, et al, 2010). In agreement, our data identified higher reported emotional distress in those with higher HbA1c levels. These findings emphasise the importance of taking into consideration the emotional distress correlated with the clinical outcomes of young people with diabetes; it may worsen and result in poor condition management (Nardi et al, 2008). Given the role of emotional distress in paediatric diabetes, clinical psychologists have a key role in maximising the benefits of treatment; facilitating a safe and non-judgemental space for the acknowledgement and processing of affect.
Interestingly, the mean PI-ED score reported by our study sample was below the recommended clinical threshold. This may be explained, in part, by the existing MDT in place in the clinic, which has embraced the role of clinical psychology as an essential part of effective diabetes intervention. Moreover, much of the existing literature exploring emotional distress outcomes in CYP use outcome measures containing somatic items, which are at risk of inflation when completed by CYP with chronic illness (O’Connor et al, 2016). Our use of the PI-ED eliminated this risk, thus potentially offering an explanation for the lower reported emotional distress in our study.
With these outcomes in mind, a fundamental role of the MDT is to consider the weighting of emotional distress in the management of diabetes in CYP. The source and severity of emotional distress should be identified and measured to allow accurate formulations and, in turn, more targeted patient-centred interventions.
A study by Babenko et al (2019) highlighted that QoL is highly impacted in individuals with diabetes. Interestingly, the current sample reported higher QoL scores, indicating an overall satisfactory QoL. As described with emotional distress, this outcome may be explained by the existing MDT support, which is inclusive of clinical psychology, within in the clinic.
The present study findings also highlighted that young people with a higher QoL report lower levels of emotional distress. The consistency of such findings in current literature, in conjunction with our data, demonstrates a relationship between diabetes, emotional distress and QoL. Therefore, diabetes interventions should acknowledge the impact of emotional wellbeing and QoL on this cohort, and integrate approaches targeted to improve these outcomes (Schram et al, 2009).
Additionally, our data indicate that CYP with higher HbA1c levels report lower QoL. Our findings can, in part, be explained by inconvenience resulting from increased frequency of appointments, as well as condition management causing disruption to daily routines (Rubin, 2000). This outcome demonstrates a pressing need for access to effective clinic-based interventions to improve QoL and HbA1c outcomes, and justifies our efforts to assess QoL perception in this cohort (Christie et al, 2014). If having a high HbA1c is correlated with a lower QoL, then this is another reason to consider and measure QoL in a clinic population.
While it is difficult to establish a causal relationship from correlational data, the relationship between QoL and HbA1c is so consistent that it is appropriate to assume that the relationship between metabolic control and QoL is equally important. Our findings validate the importance of monitoring QoL in this cohort, as it may uncover obstacles to effective condition management, and contribute to the attainment of treatment goals. Consultation with mental health professionals is invaluable in assisting diabetes care providers in the scoring and interpretation of QoL screening measures, and decision making around referrals for more in‐depth psychological support (Hilliard et al, 2018).
In line with our findings and ISPAD recommendations (Delamater et al, 2018), resources should be made available to include psychologists in the MDT, who specialise in the psychological and behavioural functioning of CYP with chronic health conditions. They should be available to interact with CYP at outpatient clinics to conduct assessment of psychosocial functioning and psychological wellbeing, as well as to support the diabetes team in the identification and management of psychological and behavioural difficulty. Screening for emotional distress and QoL should be routinely carried out, and target those with HbA1c levels outside of the recommended clinical threshold. It is imperative to identify emotional distress and QoL concerns in CYP with diabetes, as these may act as a barrier to the coordination of effective treatment for diabetes.
Future research should include a larger sample size, particularly of children with type 2 diabetes, to help identify whether there are any significant differences in emotional distress and QoL outcomes. This will further allow the MDT to tailor interventions based on individual need.
Conclusion
The current study has contributed to the literature by providing a more comprehensive picture of health and wellbeing in CYP with diabetes. The data support the value of attending to psychological wellbeing as worthy of individual attention in CYP with diabetes, and should not be contingent upon the sole consideration of physiological markers. Clinical, personal and psychological characteristics appear to be correlated with HbA1c control, and their identification is crucial in addressing strategies to optimise HbA1c control. A routine assessment of emotional wellbeing and QoL facilitates the identification of these factors. Having a psychologist integrated into the MDT can address the emotional and QoL-related needs of CYP with diabetes. The current findings can assist the MDT in directing resources towards those CYP who require it the most.





NHSEI National Clinical Lead for Diabetes in Children and Young People, Fulya Mehta, outlines the areas of focus for improving paediatric diabetes care.
16 Nov 2022